Search Questions

Understand the Crypto and Blockchain World
What is Minting?The process of converting digital assets into a part of Blockchain- a public ledger that remains untampered is called Minting. It is defined as a process of validating information, creating a new block, and recording the information into the blockchain.What is Forking?Blockchain forks are essentially a split in the blockchain network. The process which leads to the divergence of blockchain into two potential paths due to a change in protocol is forking. The network is open source and thus the code is available to everyone to suggest edits or improvements.What is Burning? The act of sending cryptocurrency tokens to a wallet with no private access key, where the tokens can’t be accessed by anyone and are lost forever is coin burning.What is a Gas Fee?Gas Fees refer to the transaction fees paid to the miners by the users on a Blockchain protocol for the transaction to be included in the block.What is a Cryptography?Scrambling sensitive information in the form of ordinary text into a code that can’t be read without a private key is cryptography. It is used to secure the information between sender and receiver.

Understanding the Crypto Mining
What is Mining? Mining refers to the process of solving mathematical equations by miners who are rewarded with coins or transaction fees for solving the equations. The transaction details are stored on Blockchain and the transaction is locked once the miner verifies it to be legitimate.

What Is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the upcoming third generation of the internet where websites and apps will be able to process information in a smart human-like way through technologies like machine learning (ML), Big Data, decentralized ledger technology (DLT), etc. Web 3.0 was originally called the Semantic Web by World Wide Web inventor Tim Berners-Lee and was aimed at being a more autonomous, intelligent, and open internet.SourceThe Web 3.0 definition can be expanded as follows: data will be interconnected in a decentralized way, which would be a huge leap forward to our current generation of the internet (Web 2.0), where data is mostly stored in centralized repositories.

What is Decentralized Autonomous Organization?
Decentralized Autonomous OrganizationDAO stands for decentralized Autonomous Organization. It is defined as a company or an organization that is not controlled by a single institution or managing staff. DAO refers to an organization where all the processes are automated and based on open-source programming code often viewed and used by anyone in the network. Designed to be Automated and decentralized, DAO is an organization structure without a board of directors and management. With an aim to eliminate human error or investor manipulation, DAO is specially designed with all the rules embedded into the code thus removing the hierarchy hurdles and bureaucracy.
Understand Evolutions in Blockchain
The wide adoption of Blockchain has led to researchers and contributors continuously upgrading this open-source technology. In the present scenario, we have witnessed an evolution of Blockchains for a decade right from the currency to the centralized systems. Let's dig deep to understand the evolution of blockchain from Generation one to the current third generation. Generation 1 Blockchain:Bitcoin is the best example of the generation one blockchain which was used for peer-to-peer currency exchange. That was the only basic purpose of the blockchain in the first generation. Litecoin and Monero are some examples of first-generation blockchains.Let’s name Generation 1 Blockchain as Peer to Peer Generation.Generation 2 Blockchain:At the early adoption of bitcoin, ethereum was launched which disrupted the cryptocurrency market. As ethereum came up with the addon over the blockchain which is smart contracts.Smart contracts enabled blockchain to level up with the use case which was limited only to currency exchange. People could develop applications using smart contracts on the blockchain.Let’s name Generation 2 Blockchain as Smart Contracts enabled Generation.Generation 3 Blockchain:Generation 3 Blockchain was again a motivation because of the drawbacks of the previous generation. People could create the applications but it tested the transaction speed of the Blockchain which was not ready to serve the response that it got. The Foundation of the new blockchains was to overcome this problem and solve the issue of scalability. Solana, Cardano, and Polkadot are some of the Third Generation Blockchains.Let's name Generation 3 Blockchain as Scalable Blockchains.If the above information has kindled your interest then, subscribe to our mailing list and share the information with your network. RWaltz Software is a leading development company in the space of Crypto and Blockchain and has Dev Team that keeps itself updated with the new technologies flooding the market. If you are looking for crypto or blockchain application development, you are moments away to get the best team in this diverse concept. Reach us today in any medium of your choice.
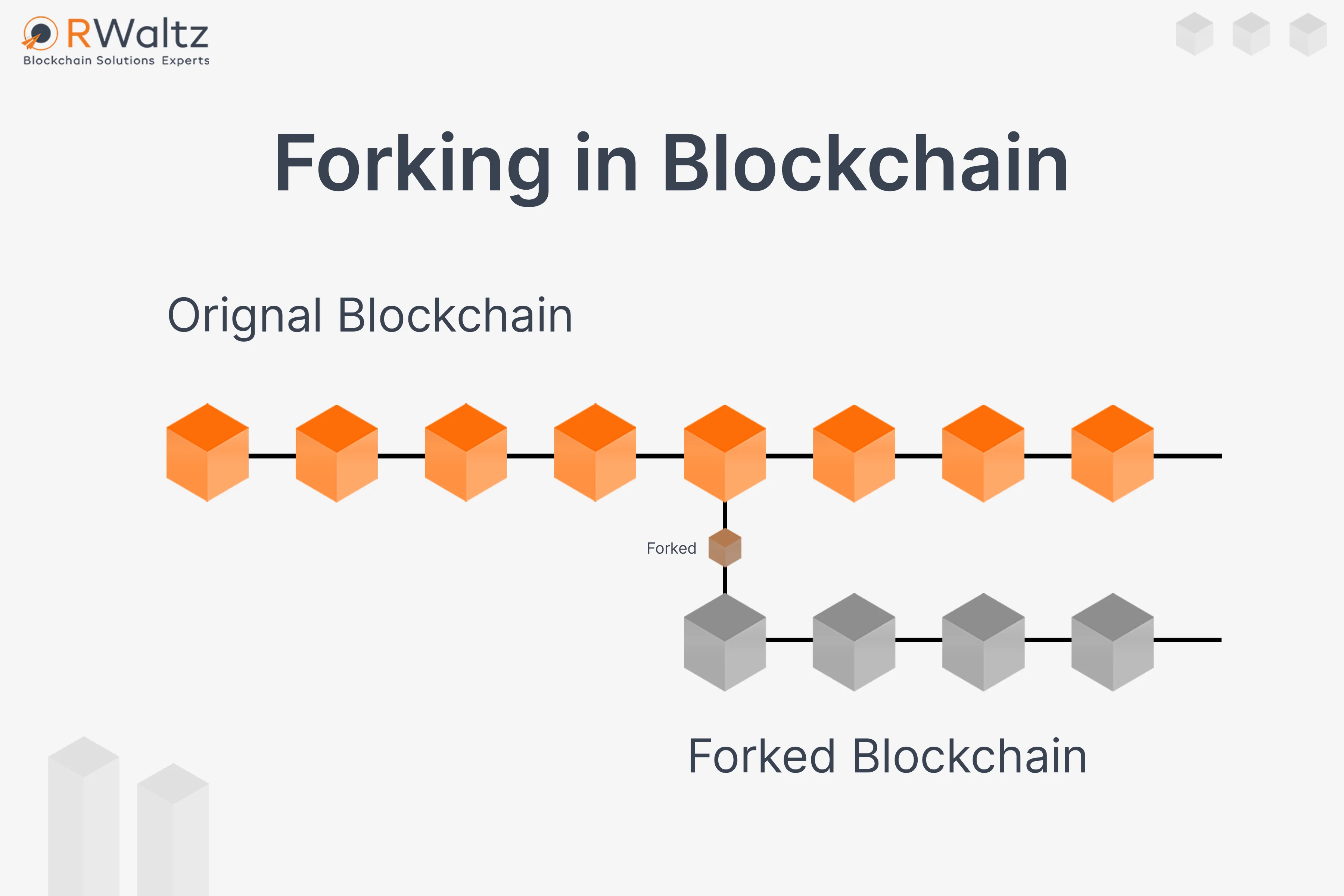
Understanding Forking and its Types
A Fork takes place whenever there is a change in the Blockchain protocol or basic rules. This change in the protocol splits the chain creating a second Blockchain. Thus, Blockchain forks are defined as a split in the Blockchain network. Forks take place when the software of different miners is misaligned. The decision to choose Blockchain resides with the miners and if it isn’t unanimous, then two versions of Blockchain are formed.Types of ForksHard ForksA hard fork is defined as a radical change to the software ensuring users upgrade to the latest software version. It is a change in the rules such that software validation based on old rules will have the blocks created according to the new rules as invalid. Hard fork involves, all nodes upgrading their software based on new rules. In case, one group uses the old software while the other use new software, a permanent split may take place. Soft Forks A soft fork is defined as a change in Blockchain which might occur when old nodes don’t follow a rule that is followed by the new nodes. It is backward compatible. A soft-fork involves the upgraded blockchain validating the transactions, where the nodes that are not updated will still see the blocks as valid. Temporary ForkWhen multiple miners mine a new block simultaneously, the network might not agree to the new block choice. Some may agree to a block mined by one party while others may agree to the alternatives available. This situation occurs because it takes some finite time for the propagation of information across the network which may lead to conflicts in the chronological order of events.We hope that the above KB has enlightened you on Forking and its types. Are you looking for Enterprise Blockchain Development? Scroll yourself to our services and schedule a meeting right away to take your project ahead with RWaltz - A Enterprise Blockchain Development Company.

Front-Running Attacks in Blockchain
Blockchain Development is gaining popularity but, at the same time attackers are finding innovative strategies to crack the transactions on it. Transactions in Blockchain are broadcasted to the network, where the miners select transactions and validate them into a valid block. This block is later added to an immutable chain of blocks where the transactions are visible to the nodes before the miner processes the transaction and it is propagated to the nodes. This is where the front-running attack comes into the picture.What is a front-running Attack? During this process, a malicious node can see the transaction, identify its purpose and send its own malicious request based on the initial transaction. Taking advantage of this process, the attackers add transactions to the blocks based on transaction fees. The attacker ensures his transaction processes before any other transaction by integrating a higher transaction fee with it. This is called a front-running attack in Blockchain. Which are the possible Front-end Attackers? Miners Miners can control the order of transaction execution and hence can conduct these attacks. They can blend their transactions without broadcasting them. Full Nodes Full nodes can see unconfirmed transactions. For Ethereum, gasPrice is a crucial factor for a profit-motivated miner to prioritize orders. The higher the gasPrice more the chances of transactions being selected. Thus, any Ethereum full node can front-run pending transactions by sending its own modified transactions with a higher price. How to Mitigate these front-running Attacks in Blockchain?Front-running is the integral feature of Blockchain Development and transaction fees are a crucial part of this environment, thus its ability to pay for priority is not an implementation error. The easiest way to escape front-running attacks is to pay transaction fees high enough then the attackers. But this solution is expensive and thus is an unsustainable way of getting rid of these attacks. Transaction SequencingThis method helps to tackle the asynchronous behavior of transactions. Ethereum selects these transactions that are stored in pending transaction pools while creating blocks. The transactions don’t have a predefined order for selection but, the miners can put them in arbitrary sequence. Since there are no rules, profits are possibly the primary reasons for miners to choose transactions from pools. FIFO (First-in-First-Out) is not-feasible for distributed ledgers since the order of transactions is not fixed. Thus, we have an alternative that is a trusted third party, that can be used to assign sequential numbers to transactions. But, this conflicts with Blockchain technology’s core innovation of distributed trust possibly adding a single point of failure. This can lead to an additional delay in the transaction validation process. Another alternative to this is sequencing transactions pseudo-randomly which is spotted in Bitcoin’s Canonical Transaction Ordering Rule. This rule makes front-running attacks statically difficult by adding a security layer and the system won’t be immune to these attacks. Zero Knowledge Proof Zero Knowledge Proof is an encryption protocol with probabilistic assessment. ZKP is a cryptographic method used to prove a specific piece of information without revealing the content of that knowledge. Zero Knowledge Proof of Work or Zero Knowledge Proof of Computation comes into the picture when a prover convinces the verifier about the correct execution of computation on secret data, without unveiling the confidential information. Wrap UPHopefully, the above article has enlightened your knowledge of front-running attacks and their remedies. If you have any queries related to Enterprise Blockchain Development, feel free to connect us. Are you looking for Enterprise Blockchain Development Services? Scroll yourself to our services and let’s take your project ahead.
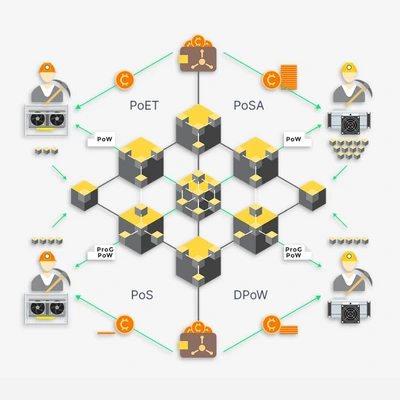
Terminologies You Should be Aware of Under Consensus Algorithm
Blockchain is distributed decentralized network offering immutability, privacy, security, and transparency. There is no central authority governing the Blockchain, yet every transaction in Blockchain is secured and verified. Here, the consensus mechanism plays a crucial role. What is Consensus Algorithm? A consensus algorithm in Blockchain Development depicts a process that is used to avail agreement on a single data value among distributed processes or systems. This algorithm is used only in distributed systems. The consensus algorithm expects a reply from 51% of resources at a time to ensure the whole system is fault-tolerant. What is Proof of Work (PoW)?Proof of work is defined as a consensus mechanism used to validate the alphanumeric codes called hash, which is calculated by the miners. Every time a new block is added to the Blockchain network, proof of work is used to verify the recent transactions. With Proof of Work (PoW), miners are completing mathematical puzzles to earn the mining rewards. What is Proof of Stake (PoS)? Proof of Stake is termed as a consensus algorithm that determines who will validate the next block based on how many coins the user is holding. Proof of stake is used to avoid the computational cost involved in proof of work. Here, the validators don’t collect the block rewards instead, they receive network fees as their rewards. What is Delayed Proof of Work (DPoW)? Delayed Proof of work (DPoW) depicts a hybrid consensus mechanism that enables one blockchain to leverage the security offered through the hashing mechanism of secondary blockchain. It is a security mechanism that is generally defined as the modified version of Proof-of-Work algorithm. The primary blockchain on DPoW might use PoW or PoS consensus, while the secondary blockchain will use PoW consensus mechanism.What is Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)? Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) is one of the fairest consensus mechanisms that chooses the next block through fair means. PoET is widely used for permissioned Blockchain Development. This algorithm offers a fair chance of creating its own block for every validator on the network. All nodes wait for a random amount of time and add proof of their wait in the block, broadcasting the created blocks to the network. What is Proof of Stake Authority (PoSA)? Proof-of-Stake Authority (PoSA) is a hybrid consensus mechanism that is a combination of both Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Authority. It supports smaller block time and lowers costs that comes at the cost of network decentralization and security. This mechanism is mostly used by Binance Smart Chain. What is Proof of Capacity (PoC)? The Proof of Capacity (PoC) mechanism allows the validators to invest their hard drive space instead of burning coins and investing in expensive hardware. The mechanism depicts that the more the hardware space the validators have better are the chances of being selected for mining the next block and earning the block reward. Wrap Up Hopefully, the above article has enlightened your knowledge of Consensus Mechanisms for Enterprise Blockchain Development. For further query, connect to our experts.If you are looking for an Enterprise Blockchain Development Company, take a look at our services. Schedule a meeting with us and lets take your project ahead.

Insightful Takeaways to Keep Your Tabs on DAO
The advent of Decentralized Application Development introduced the concept of DAO. According to a 2022 survey, the total market capitalization of DAO accounted for $21 Billion as of January 2022. Let’s explore more about DAO.A Deep Dive into DAO! A Decentralized Autonomous Organization or DAO is defined as a collectively owned organization that is governed over by Blockchain. It is termed to be an emerging form of legal structure with no central body governing the process and where members share a common mission. In other words, the organization doesn’t have a CEO or CFO who can manipulate or force the decision. Pre-defined rules in the Blockchain code define the organization process. Popularized through Decentralized Application Development, DAOs are integrated to formulate smarter decision-making in a bottom-up management approach. DAOs have in-built treasuries which can’t be accessed until the group has permitted to do so. Here, the decisions are governed through voting ensuring transparency and participation from all. Top 4 Reasons You Should have a Decentralized Autonomous Organization! Democratic Decision Making:Decisions in DAOs are collectively governed by a group of members instead of relying on a single entity. The decision-making process involves a voting system where all the members participate to make a smarter decision ensuring transparency. Community:DAO enables people from across the world to come together and construct a single vision. The token owners can interact with other investors through just an internet connection irrespective of their location. Unaltered Documents:No authority can access or modify confidential documents without the permission of a majority of the members of the organization. Also, alterations made will be reflected to all the members across the system. Smart Contracts: DAOs are based on self-executing contracts which contain immutable code. Smart Contracts ensure quick and convenient decision-making through the voting system eliminating the need for the physical presence of individuals. Rules and regulations, guidelines, functionalities, and contract addresses are a few details coded in the smart contract. Here’s the Working Process of DAO, You Might be Curious to Know! DAOs are based on smart contracts, which are logically coded self-executable agreements ensuring smarter decision-making. The decisions are powered by the underlying activities on the blockchain. These contracts are highly verifiable, visible, and auditable publicly making it easier for any potential member fully understand the functioning of protocols at every step. Once the rules & regulations are formally integrated into the blockchain, it's time to look out for a way to receive funds and the path to bestow governance. The funds are normally raised through token issuance where the protocols sell the tokens and raise funds thus filling the DAO treasury. The token holders in return for their fiats are offered certain voting rights which are generally proportional to their assets. Once the DAO treasury is filled, the DAO is ready for deployment. Once the code is published, it can’t be altered. No special authority can change the rules of DAO, it’s purely the token holder community having the right to decide it. Dapp Vs DAO- Similar or Different? Let’s Automate it! Hopefully, the DAO article was insightful for you. For any other query, you can connect us. Be fully automated and make smarter decisions powered by DAOs. If you are looking for a Decentralized Application Development Company, we are the right choice for you! Let’s automate your business with a decentralized move. Hurry up! Launch your DApp now!

White Paper- The Crux of Blockchain Projects!
White Papers have turned out to be popular and powerful weapons for Blockchain Developers. A wide array of Blockchain Development Service providers are drafting white papers to present their solutions and their benefits to investors. Let’s dive in to explore white paper. How Do You Define White Paper for Blockchain Development? A white paper refers to a document released by developers that outlines in-depth information about a specific Blockchain solution. It highlights the problems addressed, solutions offered, benefits, and Blockchain technology used. The White paper also contains different forms of data like stats, diagrams, and formulas that explain the working of smart contracts for the specified Blockchain solution. Checklists You Should Consider While Writing a White Paper for Blockchain Solutions! 1) Introduction to the Project The white paper must begin with an introduction to your blockchain project and must outline the problems the project is willing to resolve. Also, the overview should indicate the solution the readers can expect from the project. Make the overview more engaging by specifying the benefits of the blockchain solution. 2) Write the Disclaimer Many Blockchain Development Service providers offer white paper drafting as a service but very few of them specify the disclaimer in the document. The disclaimer section should introduce the legal information of the Blockchain project. This section includes legal notice or restrictions applicable to the project. 3) The Motivation Behind the ProjectThe reason for developing this project should form the crux of this section. This segment gives a brief understanding of the problem the project aims to resolve and also describes how this Blockchain solution stands out in the market. The market research and statistics will depict the exact need for the project in the existing market. 4) Real-world Utility of the Blockchain Project A variety of Blockchain projects are deployed for a wide array of industries based on their needs. The utility of Blockchain projects varies from the finance industry to supply chain management. So, it is mandatory to specify the industry the Blockchain project is serving and how it is adding value to the business.5) Tokenomics Most Blockchain projects launch tokens and thus the whitepaper should have a section to specify Tokenomics. This section explains the working and distribution of tokens. However, make sure the Tokenomics of the project’s token is explained in-depth and it makes investors less speculative about the Blockchain project. This section should present the value to the market and distribution to investors, developers, crypto enthusiasts, etc.To understand Tokenomics in detail, click here - 6) Consensus Mechanism This refers to the most critical part white paper, where the Blockchain developers specify the consensus mechanism used for the project. There are various types of consensus mechanisms like proof of work, proof of stake, etc. Specify the consensus mechanism and why it was preferred for the project. Explain the benefits of the consensus mechanism used and how it is different from others.To explore more about consensus mechanisms and their types, click here. 7) Roadmap This section explains the scope of the project in the future. The investors too are keen to understand the future of your project i.e. for how long it will sustain in the market. So, describe the goal of the project and plans which are achievable and not exaggerated. 8) Blockchain Technology Specify the Blockchain technology the project has been built on. Also, mention the benefits of leveraging the technology and how it stands different from other Blockchains. 9) Team Members who have worked Don’t forget to mention the team, who has worked hard on the project. The team of developers and testers should receive their share of the limelight. Add bios and photos of the team members who have worked on the project. Wrap Up Hopefully, the above article has enlightened your knowledge of white paper. If you are looking for a Blockchain development company, make sure the company also offers whitepaper drafting for your project. RWaltz is one such company! Dive in to explore our Blockchain Development Services, and connect to our experts now.
Understanding Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) in Blockchain
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a key component of blockchain and serves as the foundation for recording transactions and data on a decentralized network. DLT allows multiple participants to securely access, verify and update a shared ledger of transactions without the need for a central authority. Let's take a deeper look at how DLT works and its role in enabling blockchain innovations.What is a Distributed Ledger?A distributed ledger is a database that is consensually shared and synchronized across multiple sites, institutions or geographies. It allows transactions to have multiple identical copies maintained on multiple computer nodes in a network. Any changes or additions made to the ledger are reflected and copied to all participants in real-time.Unlike traditional centralized ledgers which rely on a central administrator, distributed ledgers have no central point of data storage or administration. The ledger records are stored in a decentralized manner across the network, eliminating single points of failure. This enhances security, transparency and trust in record keeping.Key Properties of Distributed Ledger TechnologyDecentralization: The ledger is distributed among participants without needing centralized control. This eliminates intermediaries, reduces costs and enhances reliability.Consensus: Changes to the ledger are validated through a consensus mechanism agreed upon by the network participants. This maintains integrity of the shared ledger.Provenance: The ledger provides a chain of custody for transactions, enabling participants to trace the origin and ownership history of assets.Immutability: Once data is recorded on the shared ledger, it cannot be altered retroactively. This creates permanent and tamper-proof records.Finality: Approved transactions are final when consensus is reached and cannot be reversed. This provides transaction certainty.Cryptography: Cryptographic techniques like digital signatures, hashing and Merkle trees secure the ledger contents and validate transactions.Types of Distributed Ledger TechnologyThere are mainly three types of distributed ledger technology: Blockchain: This is the most common form of distributed ledger technology. Transactions are recorded in consecutive blocks which are chained together chronologically to create permanent and immutable records. It enables peer-to-peer transfer of value without intermediaries. Bitcoin is the most well-known application of blockchain. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG): This uses a DAG data structure to record transactions across multiple channels simultaneously. Unlike blockchain's sequential structure, DAG enables faster transactions and no transaction fees. IOTA and Nano are examples of DAG-based DLT. Hashgraph: This uses a patented gossip protocol that allows nodes in a network to efficiently share transactions via gossip. It offers faster consensus and throughput compared to blockchains. Hedera Hashgraph is a leading hashgraph-based distributed ledger.How Distributed Ledger Technology WorksThe key steps involved in a distributed ledger network include: Initialization: The participating nodes begin by establishing a peer-to-peer network, rules of participation, consensus mechanism, cryptography standards, governance protocols etc. Transaction request: A node requests a transaction like transfer of assets which is digitally signed and broadcast to the network. Validation: Network nodes validate the transaction according to predefined rules. Invalid transactions are rejected. Consensus: The valid transaction is added to a new block or entry which is shared across nodes to confirm its validity via a consensus mechanism. Recording: Once consensus is reached, the approved transaction is timestamped and irreversibly recorded in the shared ledger. Finality: The transaction is complete, altering the states of the participating accounts or assets permanently. Reconciliation: All copies of the ledger are updated and reconciled in real-time across the distributed network.Consensus Models in Distributed Ledger TechnologyConsensus refers to the process by which participants in a distributed ledger agree to validate transactions and record new data. Some common consensus mechanisms include: Proof-of-work - Participants prove through computational work that they have invested resources to validate transactions. Used in Bitcoin. Proof-of-stake - Selects validators based on the stake they hold in the network's assets to validate transactions. Used in Ethereum. Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) - Enables nodes to reach consensus via voting by exchanging messages between nodes. Used in Hyperledger. Proof-of-Authority - Uses approved validators chosen based on reputation to validate transactions and blocks. Used in private blockchains. Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) - Enables asynchronous and parallel transaction validation across multiple nodes with no central coordinator. Used in IOTA, Nano.Benefits of Distributed Ledger TechnologyDecentralization - Eliminates central points of failure and the need for intermediaries.Trust - Enhanced security, transparency, and audibility build trust.Efficiency - Faster, low-cost transactions and settlements compared to traditional systems.Reliability - Distributed nature increases resilience against outages or manipulation.Provenance - Maintains immutable history of asset ownership and transactions.Automation - Smart contracts enable complex business rules and workflows to be automated.Tokenization - Assets like contracts or property can be represented as digital tokens.Immutable Records - Information recorded on the shared ledger cannot be altered, deleted, or lost.Use Cases of Distributed Ledger TechnologyFinancial systems - Payments, asset transfers, capital markets, trade finance.Supply chains - Tracking goods movement, certifications, and provenance.Healthcare - Electronic health records, benefits processing, clinical trials.Government - Land registries, identity management, voting systems.Energy - Trading carbon credits, renewable energy certificates (RECs).Media - Digital content ownership and distribution, intellectual property.Real estate - Property transactions, title transfers, landlord-tenant agreements.Legal - Contracts, patents, wills, company registrations.Insurance - Claims processing, know your customer (KYC) processes.Challenges with Distributed Ledger Technology Scalability - Current limits in transaction processing and data storage need to be overcome. Interoperability - Cross-chain interaction and standards need further development. Compliance - Aligning DLT solutions with regulations remains a challenge. Usability - User experience and interfaces need improvement for mass adoption. Energy Use - Proof-of-work consensus is energy intensive. Alternatives need growth. Security - Ensuring resilience to attacks like 51% attacks remains vital. Privacy - Providing user anonymity while meeting compliance needs further work.The Future of Distributed Ledger TechnologyDLT is rapidly evolving with extensive investments in research and development. Areas of expected growth include: Enterprise adoption of distributed ledgers for streamlining business processes and data sharing. Integration of DLT, IoT, AI and machine learning to create intelligent decentralized networks. Cross-chain interoperability and atomic swaps enabling seamless transactions across ledgers. Development of decentralized data storage and cloud solutions to store massive amounts of data. Evolution of consensus protocols and governance models for public distributed ledgers. User-controlled digital identities underpinned by DLT will expand participation. Tokenization of assets like real estate, commodities, intellectual property will increase liquidity. Faster transaction speeds, scalability and energy efficiency will enhance usability. Use of directed acyclic graphs and hashgraphs as high performance alternatives to blockchain. Growth of decentralized finance built on open distributed ledgers.ConclusionDistributed ledger technology provides a revolutionary decentralized approach to record-keeping and transactions compared to traditional centralized accounting systems. By eliminating intermediaries and counterparty risks, DLT enables peer-to-peer transfer of value and facilitates collaboration at unprecedented scale. As blockchain, DAGs, hashgraphs and related innovations continue maturing, DLT promises to transform enterprise systems and business models across industries and reinvent economic coordination.As a leading blockchain development company, RWaltz specializes in leveraging distributed ledger technology to build customized decentralized solutions for clients globally. Connect with our experts to assess how DLT can transform your business!
Recent Knowledge Base
Let's Build Your Vision Together
Get Started with RWaltz Today!




